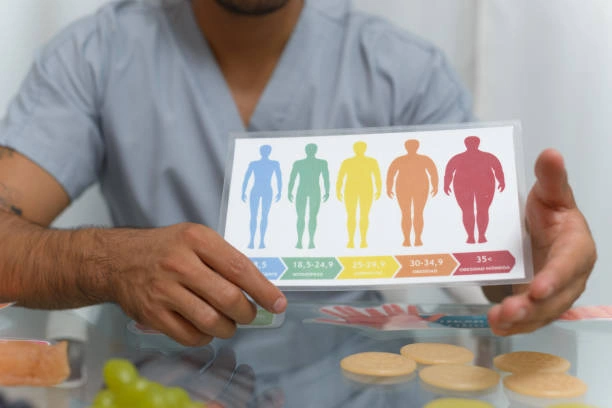
Most men don’t think much about health numbers until something feels off. A little fatigue. Jeans tighter than expected. Breath getting shorter on stairs. That’s usually when curiosity kicks in and a quick check on calculator pro starts to feel tempting. You type in height, weight, hit calculate, and suddenly a label appears. Normal. Overweight. Obese. The whole thing takes less than half a minute, yet it can linger in your head much longer.

BMI For Men often feels simple on the surface, but the reaction it creates isn’t. The number looks clean, but the meaning behind it is messier than most people expect.
Why Doctors Focus So Much on This Single Number
There’s a reason this measurement shows up everywhere. It’s fast, cheap, and easy to standardize. Doctors use it. Fitness apps show it. Insurance forms ask for it. For men especially, it often becomes the first health metric they ever see.
The appeal is speed. No blood tests. No machines. Just height and weight. But simplicity cuts both ways. The same shortcut that makes it popular also strips away context.
What BMI Actually Measures (And What It Ignores)
BMI measures mass relative to height. That’s it. It does not measure fat percentage. It does not measure muscle. It does not see bone density or water retention.
For men with higher muscle mass, this can distort results quickly. Strength training, physical jobs, or athletic backgrounds often push weight up without increasing health risk. BMI doesn’t know that difference.
Height Ratios and Why Scale Numbers Can Mislead
Two men can weigh the same and have very different BMI results depending on height. Shorter frames amplify weight changes. Taller frames dilute them. This isn’t a health judgment, it’s math.
It’s similar to measuring distance using a Temperature calculator. The tool gives an exact number, but interpretation still depends on context. BMI doesn’t provide that context on its own.
Situations Where BMI Feels “Off” for Men
- Men who lift weights regularly
- Men with dense bone structure
- Men returning to fitness after weight gain
- Men with physically demanding jobs
In these cases, BMI reacts quickly while health may not have changed much at all.
Age Changes the Meaning of the Same BMI
A BMI number doesn’t mean the same thing at 22 as it does at 42. Muscle mass slowly declines with age. Fat distribution shifts toward the abdomen. Hormones change gradually, not suddenly.
BMI doesn’t adjust for age. That’s why pairing it with context tools like an Age calculator helps frame what the number actually represents at a specific stage of life.
Informative Table: BMI Categories vs Practical Reality
| BMI Range | Category Label | What It Often Misses |
|---|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Muscle loss, nutrition gaps |
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal | Low strength, poor fitness |
| 25–29.9 | Overweight | Muscle mass, training history |
| 30+ | Obese | Fat distribution, metabolic markers |
The label shows classification, not capability.
Why Men Often Ignore BMI Until It Crosses a Line
Men tend to delay health checks. BMI often becomes relevant only after the number enters a higher category. That’s when surprise kicks in. Clothes still fit. Energy feels okay. Strength hasn’t disappeared.
The disconnect isn’t denial. It’s because BMI doesn’t capture day-to-day function. A man can perform well physically and still receive a concerning label.
BMI For Men and Muscle Mass Confusion
This is where BMI For Men causes the most debate. Muscle weighs more than fat by volume. Men naturally carry more muscle, especially in the upper body. BMI treats that weight the same way it treats fat.
That’s why some men classified as overweight or obese show excellent cardiovascular health markers. The number flags mass, not composition.
Heart Health, Fat Location, and What BMI Misses
Risk isn’t just about weight. It’s about where fat is stored. Visceral fat around the abdomen carries higher risk than fat stored elsewhere.
BMI doesn’t distinguish between the two. Waist measurements and metabolic markers often provide better insight, but the BMI calculator remains the most visible number because it’s fast.
Global Standards vs Individual Bodies
BMI categories were developed using population averages. Applying them to every individual assumes bodies behave the same way across genetics, cultures, and lifestyles.
Health metrics shift meaning across systems, similar to how financial values shift using a currency converter. The number converts, but interpretation still matters.
When BMI Is Actually Useful
Despite limitations, BMI For Men isn’t useless. It works best as a screening signal, not a diagnosis. Sudden changes, sharp increases, or consistent upward trends can signal something worth investigating.
It’s most useful when combined with:
- Blood pressure
- Waist circumference
- Activity level
- Family history
On its own, it’s incomplete.
Men vs Women: Same Scale, Different Outcomes
Men and women use the same BMI thresholds, yet body composition differs. Men generally hold less essential fat and more muscle. Using identical cutoffs simplifies comparison but reduces precision. This doesn’t make BMI wrong. It makes it limited.
How Men Should Read BMI Without Overreacting
The number should start a question, not answer it. If BMI rises slowly over years, it may reflect lifestyle drift. If it spikes suddenly, it may reflect stress, injury, or routine change. The key is trend, not label.
Final Thoughts on BMI For Men
BMI For Men works best when treated as a snapshot, not a verdict. It measures size, not strength. Mass, not movement. It can highlight patterns, but it cannot explain them. Health isn’t decided in 30 seconds. But sometimes, a quick check is enough to start paying attention.
Frequently Asked Question:
What is a healthy BMI range for men?
A healthy BMI range for adult men is generally 18.5 to 24.9. It’s a guideline used to assess potential health risks, not a diagnosis.
Is BMI accurate for men?
BMI can be useful for men, but it doesn’t account for muscle mass or body fat distribution. Men with more muscle may have a higher BMI without being unhealthy.
Why do muscular men often have a high BMI?
Muscle weighs more than fat. Men who strength train or have athletic builds can fall into higher BMI categories despite having low body fat.
Does BMI change with age for men?
The BMI categories stay the same, but body composition changes with age. Muscle mass often decreases and fat may increase, affecting how BMI reflects health.
Is BMI reliable for athletic men?
BMI can be misleading for athletic men. In these cases, waist size, body fat percentage, and fitness level give better insight.
What should men consider besides BMI?
Men should look at waist circumference, activity level, diet, cardiovascular fitness, and medical advice along with BMI for a clearer health assessment.